Nutritional Composition of Filet Mignon: Filet Mignon Nutrition Facts
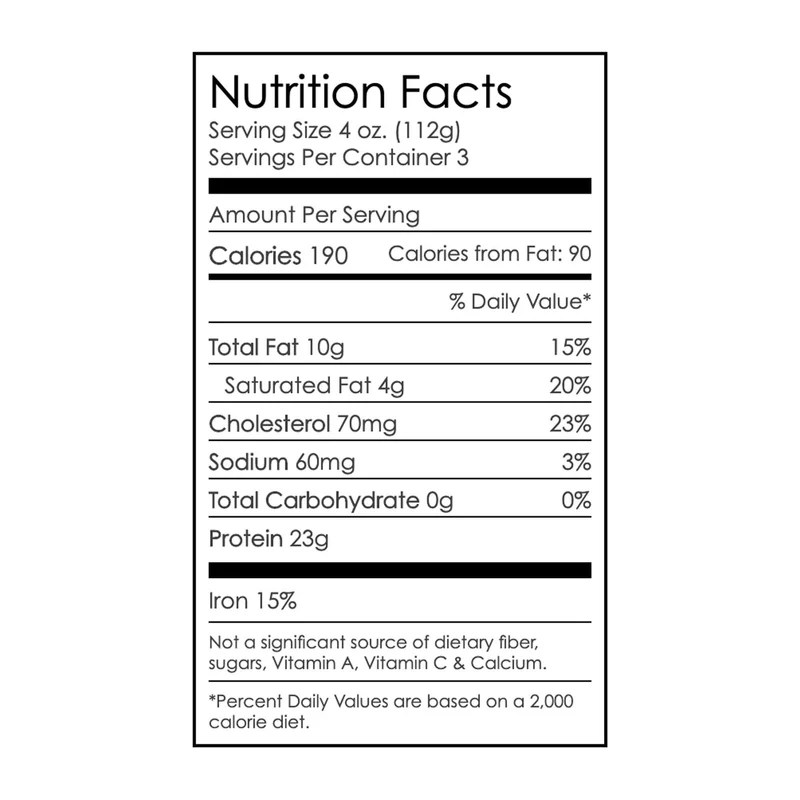
Filet mignon nutrition facts – Filet mignon, known for its tenderness and rich flavor, is a popular cut of beef. Understanding its nutritional profile is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This section provides a detailed breakdown of the macronutrients and micronutrients found in a typical serving, allowing for comparison with other beef cuts.
Macronutrient Composition of Filet Mignon
A 3-ounce serving of filet mignon generally contains approximately 190-200 calories. The macronutrient breakdown is roughly as follows: Protein constitutes a significant portion, typically around 25-30 grams, providing essential amino acids for muscle building and repair. Fat content varies depending on the cut’s marbling, but generally falls within the range of 10-15 grams, contributing to its flavor and palatability.
Filet mignon, known for its rich flavor, offers a significant amount of protein but can be higher in fat compared to other cuts. For a lighter, protein-rich alternative, consider checking out the nutritional information for oikos triple zero yogurt nutrition facts which offers a healthier contrast. Returning to filet mignon, portion control is key to managing its caloric intake within a balanced diet.
Carbohydrates are negligible in filet mignon, usually less than 1 gram per serving. While the exact percentages of daily value will vary depending on individual dietary needs and overall caloric intake, a 3-ounce serving of filet mignon provides a substantial amount of protein and a moderate amount of fat, contributing a notable percentage of daily protein requirements for many individuals.
It is important to note that the fat content can significantly influence the overall caloric value.
Micronutrient Content of Filet Mignon
Beyond macronutrients, filet mignon offers a range of essential micronutrients. It’s a good source of iron, crucial for oxygen transport in the blood. It also contains zinc, vital for immune function and wound healing. Smaller amounts of various B vitamins, such as B12 (important for nerve function and red blood cell formation), are also present. The specific amounts of these micronutrients can fluctuate slightly based on factors such as the animal’s diet and rearing conditions.
However, filet mignon consistently provides a contribution to the daily recommended intake of several essential vitamins and minerals.
Comparison of Filet Mignon with Other Beef Cuts
The following table compares the nutritional values of filet mignon to other popular beef cuts, per 3-ounce serving. Note that values can vary based on preparation methods and marbling.
| Beef Cut | Calories | Protein (grams) | Fat (grams) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filet Mignon | 195-210 | 26-29 | 12-15 |
| Ribeye | 220-240 | 24-27 | 18-21 |
| Sirloin | 180-200 | 25-28 | 8-11 |
Health Implications of Filet Mignon Consumption

Filet mignon, prized for its tenderness and flavor, presents a complex nutritional profile with both benefits and drawbacks for health-conscious consumers. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed dietary choices and incorporating this luxury cut into a balanced eating plan. While it offers certain nutritional advantages, mindful consumption is key to mitigating potential negative impacts.Filet mignon is a rich source of high-quality protein, essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and maintaining overall bodily processes.
It also contains various essential nutrients, including iron, vitamin B12, and niacin, all vital for optimal health. However, its high saturated fat and cholesterol content necessitate careful consideration within a broader dietary context.
Protein Intake and Essential Nutrients in Filet Mignon
Filet mignon provides a significant amount of protein per serving, contributing to satiety and aiding in muscle maintenance and growth. The protein in filet mignon is highly bioavailable, meaning the body efficiently absorbs and utilizes it. Furthermore, the presence of essential B vitamins, such as B12 crucial for red blood cell formation and neurological function, and niacin, which plays a role in energy metabolism, adds to its nutritional value.
Iron, another component, supports oxygen transport throughout the body. A balanced diet incorporating leaner protein sources alongside occasional filet mignon consumption can ensure adequate intake of these essential nutrients.
Potential Drawbacks of Regular Filet Mignon Consumption
The high saturated fat content in filet mignon is a significant consideration. Saturated fats can contribute to elevated LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. Similarly, the relatively high cholesterol content adds to this concern. Regular consumption of foods high in saturated fat and cholesterol may negatively impact cardiovascular health, particularly for individuals already at risk.
Therefore, moderation is key to mitigating these potential drawbacks.
Comparison with Alternative Protein Sources, Filet mignon nutrition facts
Choosing protein sources wisely is vital for maintaining a balanced diet. Comparing filet mignon’s nutritional profile with alternatives such as chicken breast and fish highlights its strengths and weaknesses.
- Filet Mignon: High in protein, iron, B vitamins; high in saturated fat and cholesterol.
- Chicken Breast: High in protein, low in fat and cholesterol; lower in iron and B12 compared to filet mignon.
- Fish (e.g., Salmon): High in protein, omega-3 fatty acids; lower in saturated fat and cholesterol than filet mignon; good source of vitamin D.
While filet mignon offers a unique taste and nutritional benefits, incorporating it into a balanced diet that includes leaner protein sources like chicken breast and fish is recommended for optimal health. The occasional indulgence in filet mignon is unlikely to pose significant health risks for most individuals, but regular consumption should be approached with awareness of its saturated fat and cholesterol content.
Top FAQs
Is filet mignon a good source of iron?
Yes, filet mignon is a good source of iron, an essential mineral for oxygen transport in the blood.
Can people with high cholesterol eat filet mignon?
Individuals with high cholesterol should consume filet mignon in moderation due to its saturated fat content. Leaner cuts and preparation methods can help mitigate this concern.
How many calories are in a 3-ounce serving of filet mignon?
The calorie count varies depending on preparation, but a 3-ounce serving generally contains between 180-250 calories.
Is filet mignon suitable for a ketogenic diet?
Yes, filet mignon is generally suitable for a ketogenic diet due to its high protein and low carbohydrate content. However, portion size and added ingredients should be considered.
What are some healthy ways to prepare filet mignon?
Healthy preparation methods include grilling, broiling, or pan-searing with minimal added fats or sauces. Consider herbs and spices for flavor instead of heavy sauces.
